Corrosion protection
Corrosion is one of the most common reasons for vehicle breakdowns. In many cases, damage is only noticed when it is too late. To extend the life of your car and avoid expensive repairs, it is important to take preventive measures. We'll explain here how rust develops and what you can do about it.
When and where corrosion happens
Modern vehicles are often designed with special openings in doors and other cavities that drain away moisture to prevent rust from developing. However, a certain amount of residual moisture will always remain, which damages your car's bodywork in the long term. In addition, the drains can become clogged with leaves or other debris. This results in waterlogging as the water cannot drain away– the ideal environment for corrosion to develop.
Most manufacturers protect the bodywork and underbody of their vehicles at the factory by applying various coatings and paints. However, depending on various circumstances, these can become less effective over time. Even vehicle galvanization, which is standard practice for some manufacturers, unfortunately does not provide 100 percent protection against corrosion.
Causes of corrosion
Stone chips and scratches
By damaging the protective layer of the paintwork, stone chips and scratches expose the metal and open the way for damaging moisture to penetrate the bodywork. Depending on how many layers of paint are damaged, this can be very inconspicuous at first. However, after a while, sometimes even years later, this damage can become noticeable in the form of rust.
Regional/climate conditions
Vehicles in dry and warm regions are less susceptible to rust than those in cold regions with a lot of moisture. The quality of the roads also plays a major role in terms of stone chips and scratches.
Salt in winter
The use of adhesion-enhancing gritting agents increases corrosion. The de-icing agent adheres to the bodywork, giving the salt enough time to attack the protective layer of the paint.
Rust-prone areas
In principle, this is any area where water can accumulate or which is permanently exposed to moisture. For example, this could be drainage channels, gaps, ridges, edges, joints and cavities.
- This includesdoors, wheel wells, tailgates, and so on.
Bodywork components with cavities where moisture accumulates become typical corrosion spots.
- Behind plastic paneling
Moisture accumulating here ensures that even small impurities between the plastic and steel act like sandpaper, rubbing off the protective paint layer and setting the stage for corrosion.
- Hinges, axles, joints, etc.
While the bodywork is generally more effectively protected thanks to galvanization, other parts on the underside of the vehicle are very susceptible to rust and are permanently exposed to moisture.
- Front and hood
Despite galvanizing, those body parts with an increased risk of stone chipping are particularly susceptible.
- Windows and sunroofs
Moisture gets behind seals and trim strips, where it has difficulty drying, resulting in small corrosion blisters on the paintwork.
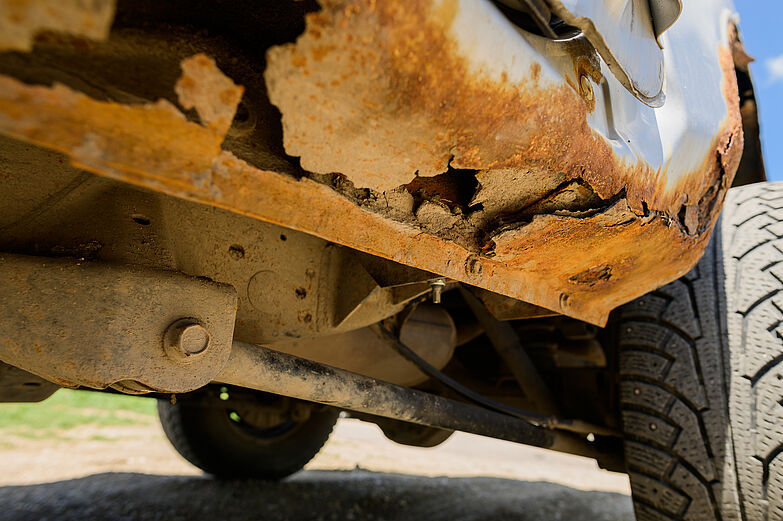

Why corrosion protection is vital
Professional corrosion protection pays off! Otherwise, you are at risk for:
- severe, irreparable damage to bodywork components
- expensive and time-consuming repairs
- problems during a general inspection
- adverse effects on your vehicle's stability
- premature loss of value

Advantages of rust protection
- long-term value retention of bodywork and vehicle
- protection from environmental factors
- helps avoid the need for costly repairs
How to prevent rust on your vehicle
To optimally protect your vehicle against rust and other types of corrosion caused by moisture, salt, dirt or chemicals on the roads, you can adopt various measures (usually in combination).
Above all, regular bodywork maintenance and servicingis particularly important. Touching up stone chips and scratches can help to prevent corrosion and the resulting damage it causes.
You can also actively prevent corrosion on your vehicle on your own. Clean and maintain your vehicle regularly, to remove any dirt and salt deposits that can lead to corrosion. For this, we also offer all the essential products in our maintenance range.

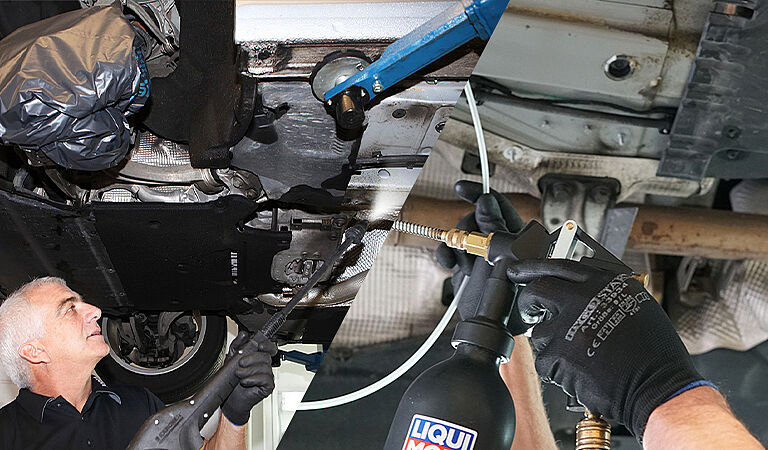
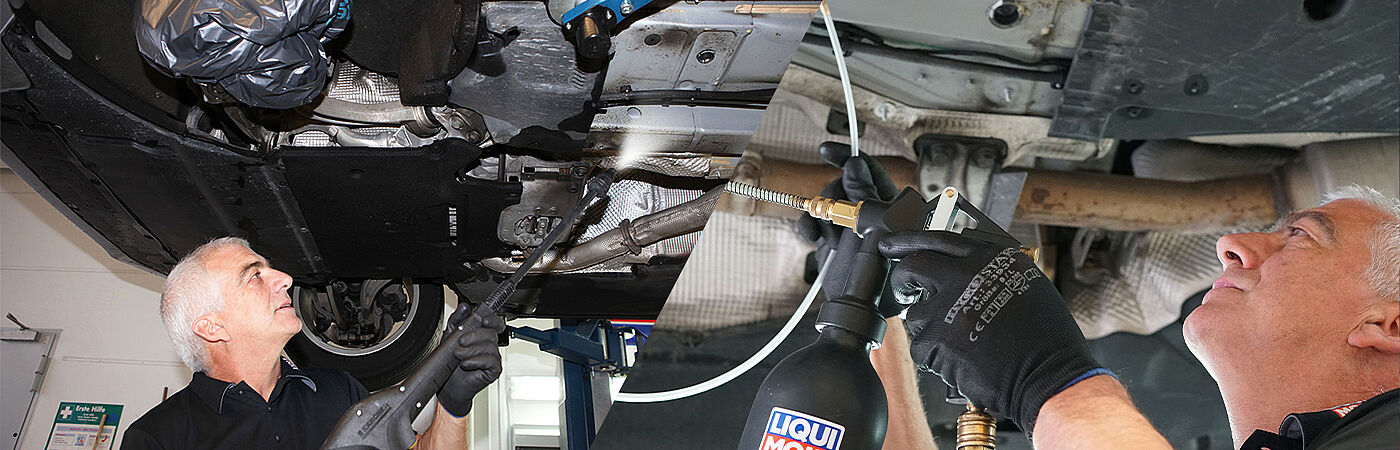
Corrosion prevention through protective coating on metal surfaces and underbody
One of the most common methods is to apply a protective coating to the metal and underbody of the vehicle, for example by using special coatings, waxes or other surface treatments.
- protects against minor surface damage (e.g., stone chips) and therefore rust
- prevents moisture from coming into direct contact with metal
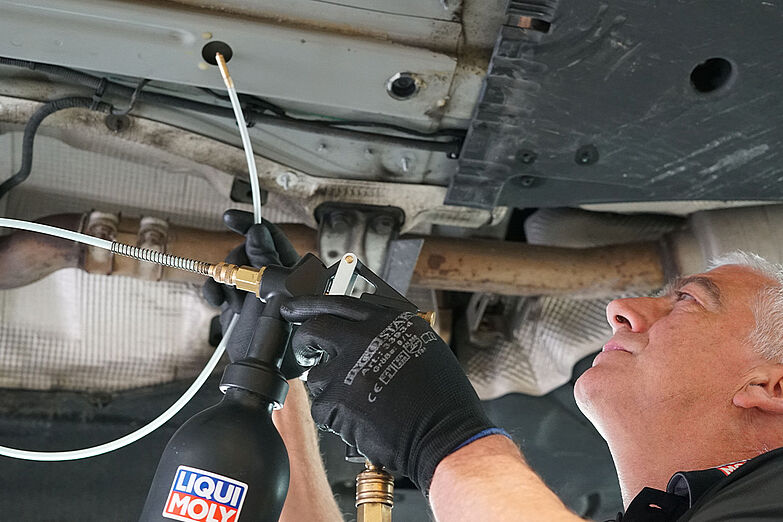



Corrosion protection thanks to cavity sealing
You can also seal cavities in doors, wheel wells, tailgates, etc. to provide the best possible protection for metal and body parts against moisture build-up, thereby preventing rust.
- prevents moisture and debris from accumulating in places you cannot reach