Classifications and specifications
The classification of all types of oil ensures consistent quality and functionality of lubricants internationally. This standardization makes it possible to make specific statements about the requirements for the lubricants.
Specifications, on the other hand, depend on the manufacturer and indicate which engine or gearbox the lubricants are compatible with and officially approved by the vehicle manufacturer.

Motor oil classification
In order to select the correct motor oil, two pieces of information are required: viscosity and quality. There are several organizations for this classification of motor oil:
- SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers)
- ACEA (European Automobile Manufacturers Association)
- API (American Petrol Institute)
- ILSAC (International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee)
- JASO (Japan Automobile Standards Organization)
The well-known European vehicle and engine manufacturers (Mercedes-Benz, BMW, VW, etc.) use SAE viscosity specifications and ACEA quality specifications.
The motor oils to be used for import vehicles developed outside Europe (Toyota, Mitsubishi, Chrysler, etc.) are also based on SAE for viscosity specifications and mainly on API or ILSAC for quality specifications. For diesel vehicles with DPF increasingly also in accordance with ACEA.
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers)
The Society of Automotive Engineers classifies oils exclusively according to limit temperatures at which a certain flow behavior (viscosity) must be demonstrated. However, viscosity only provides information about the fluidity (internal friction) of an oil and does not define any qualitative properties. An oil with SAE classification therefore only has a specified flow behavior at different temperatures.
Cold start range viscosity is indicated with the letter “W” (e.g. 5W). The smaller the number before the “W”, the more fluid the oil is at low temperatures. The number without a letter (e.g. 30) indicates the operating temperature range. The higher the number, the thicker the oil when measured at 100 °C.
Up to which low temperature a motor/gearbox oil can be used depends on the flowability in the limit temperature range. The deeper the expected temperature, the less viscous the oil has to be.
This is how long it takes for the engine oil to reach the last lubrication point during a cold start (0 °C):
| Viscosity 0W-XX | Viscosity 5W-XX | Viscosity 10W-XX | Viscosity 15W-XX |
| 2.8 seconds | 8 seconds | 28 seconds | 48 seconds |
| SAE 0W | - 40 °C |
| SAE 5W | - 35°C |
| SAE 10W | - 30°C |
| SAE 15W | - 25°C |
| SAE 20W | - 20 °C |
| SAE 25W | - 15 °C |
(max. 150,000 mPa*s)
| SAE 70W | - 55°C |
| SAE 75W | - 40 °C |
| SAE 80W | - 26 °C |
| SAE 85W | - 12°C |
ACEA (European Automobile Manufacturers Association)
The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association is the oil standard for European vehicle and engine manufacturers. The ACEA classification distinguishes between oils for gasoline engines (A), passenger car diesel engines (B), passenger car gasoline and diesel engines with exhaust aftertreatment systems (e.g. particulate filters) (C) and commercial vehicle diesel engines (E). Each category has its own meaning and cannot be used in a backwards-compatible manner.
At the end of 2018, the ATIEL (interest group representing the knowledge and experience of engine oil manufacturers and marketers) stipulated in the “Letter of Conformance” that ACEA A / B may not be advertised on an oil in conjunction with ACEA C specifications, as the components (e.g. ash content, etc.) are too different. This meant that all ACEA A/B specifications had to be removed from ACEA C oils.
| A1/B2 | High performance engine oil for gasoline and diesel engines, fuel economy engine oil with particularly low high-temperature high-shear viscosity (2.9 – 3.5 mPA*s). Reserved for viscosity class xW-20. Not valid since 12/2016. |
| A3/B4 | High performance engine oil for gasoline and diesel engines, surpasses and replaces conventional engine oils such as ACEA A2/B2 or A3/B3 and can be used for extended change intervals. |
| A5/B5 | High performance engine oil for gasoline and diesel engines, fuel economy engine oils with particularly low high-temperature high-shear viscosity (2.9 – 3.5 mPa*s). Reserved for viscosity classes xW-30. |
| A7/B7 (NEW) | High performance engine oil for gasoline and diesel engines. For low viscosity classes (0W-x) with particularly low high-temperature high-shear viscosity (2.9-3.5 mPa*s). Based on ACEA A5/B5, it offers additional protection against LSPI, increased turbocharger cleanliness and improved chain wear protection. |
| C1 | Category for low-SAPS oil with reduced HTHS viscosity ≥ 2.9 mPa*s, performance as A5/B5, but with very limited content of sulfate ash, phosphorus, sulfur. |
| C2 | Category for low SAPS oil with reduced HTHS viscosity ≥ 2.9 mPa*s, performance as with A5/B5, with limited, but higher proportions of sulfate ash, phosphorous, sulfur compared with C1. |
| C3 | Category for mid SAPS oil with increased HTHS viscosity ≥ 3.5 mPa*s, performance as with A3/B4, with limited, but higher proportions of sulfate ash, phosphorous, sulfur compared with C1. |
| C4 | Category for low SAPS oil with high HTHS viscosity ≥ 3.5 mPa*s, low viscosity, performance as with A3/B4, with the same proportions of sulfate ash and sulfur, but increased proportion of phosphorus compared with C1. |
| C5 | Category for mid-SAPS oil with a greatly reduced HTHS viscosity of 2.6 – 2.9 mPas*s, for further improved and optimum fuel savings, for vehicles with state-of-the-art exhaust gas treatment systems, only for engines with the corresponding technical requirements. |
| C6 (NEW) | Based on ACEA C5 and has specific tests focusing on LSPI and turbocharger protection, as well as new fuel consumption tests |
API (American Petrol Institute)
The American Petrol Institute basically distinguishes between two types of engine oil, one for gasoline engines (S) and one for diesel engines (C). The letter following the first letter S or C, e.g. J or L, defines the quality of the lubricant. The later in the alphabet this letter is, the higher the quality of the motor oil. Higher-quality specifications such as API SN Plus or SP can be used without concern according to API for the previous classifications, e.g. API SM, and are therefore backwards compatible.
The latest API SP and API SN Plus also contain LSPI tests. There is also the addition “+RC” for the API SN Plus classification. This represents additional fuel savings.
For engine oils for diesel engines, a “-4” may also be listed. This addition indicates suitability for large-volume 4-stroke diesel engines such as trucks or buses (heavy duty). API CF-2 stands for the quality of a 2-stroke diesel motor oil.
In 2016, API F was introduced as a new stand-alone diesel specification for emission & fuel savings. This new specification may only be used in engines designed specifically for this purpose. API FA-4 is for xW-30 oils with reduced HTHS viscosity and is not compatible with API Cx-4 classes.
| API-SA | (up to 1930) with softening point improver and antifoam agent |
| API-SB | (after 1930) with active ingredients against aging, corrosion and wear |
| API-SC | (from 1964 to 1967) additional active agents against coking |
| API-SD | (from 1968 to 1971) for heavy-duty operating conditions in gasoline engines |
| API-SE | (from 1971 to 1979) with higher requirements for gasoline engines |
| API-SF | (from 1980 to 1987) with improved wear protection and sludge carrying capacity |
| API-SG | (from 1987 to 1993) with additional protection against (black) sludge formation |
| API-SH | (from 1993 to 1996) with additional requirements against lubricating film tearing at high temperatures and high shear load (HTHS) and evaporation loss |
| API-SJ | (from 1996) with additional requirements regarding evaporation loss |
| API-SL | (from 2001) with additional requirements for fuel efficiency ("energy-saving") |
| API-SM | (from 2004) with additional requirements for oxidation stability, engine cleanliness, wear protection, aging behavior and performance at low temperatures. |
| API-SN | (2010 onwards) for improved piston high temperature protection, tighter slurry control, higher seal compatibility. |
| SN-RC | Improved performance for lower fuel consumption, turbocharger protection, compatible with emission control systems, and protection of engines operating with ethanol-containing fuels up to E85 |
| API-SN | Plus (from 2018) Supplement to API-SN with additional requirements and LSPI test to protect against low speed pre-ignition (LSPI) in turbocharged direct injection gasoline engines. |
| API-SP | (from 2020) with additional requirements on the reduction of LSPI during the entire oil change interval, wear protection for engine and chain, protection against corrosion, compatibility with emission systems (OPF/GPF), oxidation stability, deposit monitoring, protection against sludge and painting |
| API-TA | Mopeds (obsolete) |
| API-TB | Motorcycles and scooters (obsolete) |
| API-TC | High-performance engines (obsolete, but still recognized worldwide) |
Info: NMMA TC-W3 -> 2-stroke specification for boats
ILSAC (International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee)
The International Lubricants Standardization and Approval Committee is very strongly based on the categories according to API in its classification of motor oil. There are six classification classes (GF-1 to GF-6) for gasoline engines. ILSAC does not take diesel engines into account.
| GF-1 | Introduction year 1996, comparable to API SH, category not current |
| GF-2 | Introduction year 1997, comparable to API SJ |
| GF-3 | Introduction year 2001, comparable to API SL |
| GF-4 | Introduction year 2004, comparable to API SM |
| GF-5 | Introduction year 2010, comparable to API SN |
| GF-6 | Launch year 2020, comparable to API SP |
| GF-6A (NEW) | Launch year 2020, comparable to API SP
|
| GF-6B (NEW) | Launch year 2020, comparable to API SP
|
JASO (Japan Automobile Standards Organization)
The Japan Automobile Standard Organization predominantly defines the criteria and quality standards for two-wheel oils. Here increased requirements of friction behavior (wet clutches), shear stability and burning behavior are set out. The JASO and API classifications are always occur together in the two-wheel sector. There are also specifications for passenger cars and commercial vehicles.
| JASO MA | high friction coefficient for motorcycles with wet clutch |
| JASO MA-2 | very high friction coefficient for motorcycles with wet clutch |
| JASO MB | low friction coefficient for two-wheelers without wet clutch |
| JASO FB | low cleaning, incomplete combustion |
| JASO FC | high purification, almost complete combustion |
| JASO FD | highest cleaning, complete combustion |
| DH-1 | Japanese diesel engine oil performance classification, launch year 2020 |
| DH-2 | Performance classification as DH-1, but for exhaust gas treatment systems, max. 50 ppm diesel sulfur content |
| DL-1 | Performance classification as DH-1, but especially for passenger cars with exhaust gas treatment systems, max. 50 ppm diesel sulfur content |
Gear oil classification
With the increasing number of gearbox types, gear oils have also been further developed and adapted. These are roughly divided into manual or axle drive gearbox, automatic, dual-clutch and CVT gearbox. Within these main groups, there are various subgroups, all of which require a special lubricant tailored to the design and intended use.
For gearbox oils, however, there is no uniform basis that the manufacturers are obliged to uphold (e.g. ACEA). This leads to a variety of special manufacturer approvals.
In order to at least be able to get a general answer as to what quality or which properties a gearbox oil corresponds to, division into by API for manual gearbox and axle drives and by DEXTRON for automatic gearboxes has become established. The viscosity of the manual gearbox and axle drive is – as with motor oil – classified by SAE. The viscosity of automatic gearbox oils, so-called ATF oils (Automatic Transmission Fluid), is not classified by SAE, as the viscosity is a part of the respective manufacturer approval.
The following must therefore be observed in order to select the correct gear oil: High-performance lubricants that comply with manufacturer approvals are required for the trouble-free operation of modern gearboxes. The type and quantity of additives in the lubricant has a significant influence on various parameters, such as the shifting capacity, the change interval, the friction behavior and the wear protection.
| GL 1 | Low load hypoid or worm gearbox |
| GL 2 | Worm gearbox (not in road vehicles) |
| GL 3 | Manual gearbox (vintage) |
| GL 4 | Manual gearbox, hypoid gearbox if approved |
| GL 5 | Hypoid gearbox, manual gearbox if approved |
| DEXTRON Tasa | from 1957 |
| DEXTRON B | from 1967 |
| DEXTRON II C | from 1973 |
| DEXTRON II D | from 1981 |
| DEXTRON II E | from 1991 |
| DEXTRON III F | from 1994 |
| DEXTRON III G | from 1997 |
| DEXTRON III H | as of 2003 |
| DEXTRON VI | from 2005 |
| Mercon | from 1987 |
| Mervon V | from 1996 |
| Mercon LV | from 2005 |
| Mercon ULV | from 2014 |
| Mercedes-Benz | 26 ATF approvals (MB approval 236.x) 21 (Hypoid) gearbox oil approvals (MB approval 235.x) |
| Volkswagen | 14 ATF approvals (G 052 xxx, G055 xxx, G060 xxx) 15 (hypoid) gearbox oil approvals (G 052 xxx, G055 xxx, G060 xxx) |
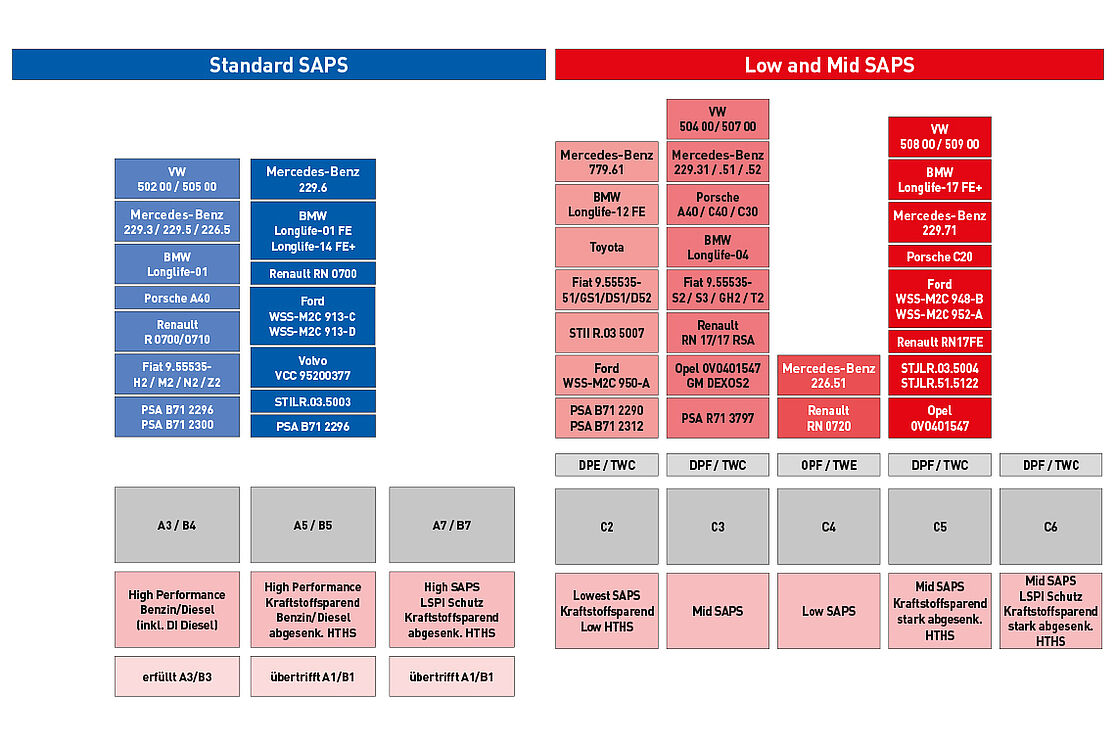
Car manufacturer specifications
European vehicle manufacturers base their prescribed manufacturer specifications on the ACEA engine tests. In order to achieve a manufacturer approval for a certain oil, in addition to the respective ACEA test procedure, further motor tests and requirements must be fulfilled.
Basic classification of passenger car manufacturer specifications
| Longlife-98 | Basis ACEA A3/B3, usable from model year ′98, is replaced by Longlife-01 |
| Longlife-01 | Basis ACEA C3, usable from model year ′01, for gasoline and diesel engines without DPF |
| Longlife-04 | Basis ACEA C3, usable from model year ′04 |
| Longlife-12 FE | Basis ACEA C2, usable from model year ′13, lowered HTHS viscosity, not backwards compatible, only for selected engines |
| Longlife-14 FE+ | Basis ACEA A1/B1, usable from model year ′14, lowered HTHS viscosity, not backwards compatible |
| Longlife-17 FE+ | Basis ACEA C5, usable from model year '14, lowered HTHS viscosity, includes Longlife -14 FE+, only for selected gasoline engines |
| Longlife-19 FE | Diesel oil specification based on ACEA C3, which was carried out with a new BMW test engine and is currently technically suitable for many engines from 2004 with Longlife-04 approval. Viscosity classes 0W-30 |
| Longlife-22FE++ | Gasoline oil specification carried out with new BMW test engine and may only be used for approved gasoline engines from MY 2022. |
| 9.55535-CR1 | Basis ILSAC GF-5 or API SN, viscosity class 5W-20 |
| 9.55535-DS1 | Basis ACEA C2, viscosity class 0W-30 |
| 9.55535-DM1 | Basis ACEA C5, fully synthetic, special development |
| 9.55535-G1 | Basis ACEA A1 or A5, viscosity class 5W-30, special development for CNG engines |
| 9.55535-G2 | Basis ACEA A3, viscosity classes 10W-40 and 15W-40, usable in older gasoline engines |
| 9.55535-GH2 | Basis ACEA C3, viscosity class 5W-40, special development for ′′1750 Turbo Engine′′ |
| 9.55535-GS1 | Basis ACEA C2, viscosity class 0W-30, special development for 0.9 Twin Air (turbo) engine |
| 9.55535-GSX | Basis ILSAC GF-5 or API SN, viscosity class 0W-20 |
| 9.55535-H2 | Basis ACEA A3, viscosity class 5W-40, suitable for extended change intervals |
| 9.55535-M2 | Basis ACEA A3/B4, viscosity classes 0W/5W-40, suitable for extended change intervals |
| 9.55535-N2 | Basis ACEA A3/B4, viscosity class 5W-40, suitable for gasoline and diesel turbocharged engines |
| 9.55535-S1 | Basis ACEA C2, viscosity class 5W-30, suitable for gasoline and diesel turbocharged engines with WIV |
| 9.55535-S2 | Basis ACEA C3, viscosity class 5W-40, suitable for gasoline and diesel engines with WIV |
| 9.55535-S3 | Basis ACEA C3, viscosity class 5W-30, special development for Chrysler, Jeep and Lancia |
| 9.55535-S4 | Basis ACEA C4, viscosity class 5W-30 |
| 9.55535-T2 | Basis ACEA C3, viscosity class 5W-40, special development for gas engines |
| 9.55535-Z2 | Basis A3/B4, viscosity class 5W-40, special development for twin turbo diesel engines |
| Abarth 0101 | No ACEA performance level, viscosity class 10W-50, special approval for Abarth engines |
| WSS-M2C-913-D | Basis ACEA A5/B5, replaces WSS-M2C-913-A, B and C |
| WSS-M2C-925-B | Basis API SM, backwards compatible with WSS-M2C-925-B, is replaced by WSS-M2C-948-B |
| WSS-M2C-917-A | Basis ACEA A3/B4, counterpart to VW 505 01 |
| WSS-M2C-934-B | Basis ACEA C1, viscosity class 5W-30 |
| WSS-M2C-925-A | Basis ACEA A1/B1, A5/B5 and ILSAC GF-3, viscosity class 5W-20 |
| WSS-M2C-925-B | Basis ACEA A5/B5, viscosity class 5W-20, heavily reduced HTHS viscosity |
| WSS-M2C-930-A | Basis ILSAC GF-4, viscosity class 5W-20, heavily reduced HTHS viscosity |
| WSS-M2C-937-A | Basis ACEA A3/B4, viscosity class 0W-40, specially for Focus RS |
| WSS-M2C-945-A & B1 | Basis ILSAC GF-5, viscosity class 5W-20, heavily reduced HTHS viscosity |
| WSS-M2C-946-A & B1 | Basis ILSAC GF-5, viscosity class 5W-30 |
| WSS-M2C-947-A & B1 | Basis ILSAC GF-5 and API SN, viscosity class 0W-20, heavily reduced HTHS viscosity |
| WSS-M2C-948-B | Basis API SN, specially developed for Ford EcoBoost engines |
| WSS-M2C-950-A | Basis ACEA C2, specially developed for Euro 6 TDCi engines, viscosity class 0W-30 |
| WSS-M2C-952-A1 | Basis ACEA C5, viscosity class 0W-20, sulfate ash content <0.8%, specially developed for 1.5 EcoBlue diesel engine (from 2018) |
| WSS-M2C-956-A1 | Basis ACEA C5, viscosity class 0W-20, similar to VW 508 00/509 00, for Tourneo Connect (from 2021) |
| MB approval 229.1 | For all passenger cars up to 03/2002, replaced by MB 229.3 |
| MB approval 229.3 | For intervals up to 30,000 km, is replaced by MB 229.5 |
| MB approval 229.5 | Stricter requirements than for 229.3, intervals up to 40,000 km possible |
| MB approval 229.31 | Requirements as for 229.3, but low in ash, replaced by MB 229.51 |
| MB approval 229.51 | Requirements as for 229.5, but low in ash, replaced by MB 229.52 |
| MB approval 229.52 | Increased requirements for oxidation stability and fuel economy |
| MB approval 229.6 | Basis ACEA A5/B5, not backwards compatible, fuel saving, only for selected engines |
| MB approval 229.61 | Basis ACEA C2 |
| MB approval 229.71 | Basis ACEA C5, heavily lowered HTHS viscosity, not backwards compatible, for selected engines only |
| MB approval 226.5 | Based on Renault RN0700 |
| MB approval 226.51 | Based on Renault RN0720 |
INFO: 2 digits after the point = ash-reduced for exhaust gas treatment systems
| GM LL-A-025 | Basis ACEA A3/B3, specification for gasoline engines, obsolete, replaced by GM Dexos2 |
| GM LL-B-025 | Basis ACEA A3/B4, specification for diesel engines, obsolete, replaced by GM Dexos2 |
| GM Dexos 2 | Basis ACEA C3, usable for all engines from model year ′10, is partially replaced by OV0401547. |
| GM Dexos1 Gen. 2 | Basis API SN-RC, viscosity classes 0W-20, 5W-20 and 5W-30 Specification for gasoline engines with direct injection and LSPI problems. |
| GM Dexos1 Gen. 3 | Expansion of the GM Dexos1 Gen.2 and is backwards compatible with this (since Opel was taken over by PSA, only valid for GM General Motors). |
| OV 040 1547 - A20 | Basis ACEA C5, viscosity class 0W-20 for gasoline and diesel engines HTHS >= 2.6 and LSPI protection, new Opel/Vauxhall specification or designation for GM dexos2 Gen.2 and GM dexos D. |
| OV 040 1547 - D30 | Basis ACEA C3, viscosity class 5W-30 new Opel/Vauxhall specification or designation for GM Dexos2 for diesel engines |
| OV 040 1547 - G30 | Basis ACEA C3, viscosity class 5W-30 new Opel/Vauxhall specification or designation for GM Dexos1 Gen.2 and GM Dexos2 for gasoline engines |
| PSA B71 2290 | Basis ACEA C2 with viscosity class 5W-30 |
| PSA B71 2295 | Basis ACEA A2/B2 for engines before model year 1998, no viscosity defined |
| PSA B71 2296 | Basis ACEA A3/B4 with viscosity classes 0W-30, 0W-40, 5W-30 and 5W-40 |
| PSA B73 2297 | Basis ACEA C3 with viscosity classes xW-30 and xW-40 |
| PSA B71 2300 | Basis ACEA A3/B4 with viscosity classes xW-40 and xW-50 |
| PSA B71 2312 | Basis ACEA C2 with viscosity class 0W-30 |
| A 40 | Basis ACEA A3 with viscosity classes 0W-40 and 5W-40, for gasoline engines from '94. |
| C 20 | Basis ACEA C5, corresponds to VW 508 00/509 00, not backwards compatible, only for selected engines. |
| C 30 | Basis ACEA C3, corresponds to VW 504.00/507.00. |
| C 40 | Basis ACEA C3, corresponds to VW 511 00, for gasoline engines with particulate filter (from MY 2019), not backwards compatible. |
| RN 0700 | Basis ACEA A3/B4, permissible for all Renault gasoline engines. |
| RN 0710 | Basis ACEA A3/B4, permissible for all Renault diesel engines without soot particulate filter. |
| RN 0720 | Basis ACEA C4, permissible for all Renault diesel engines with soot particulate filter from model year '10. |
| RN 17 | Basis ACEA C3, permissible for all diesel engines from model year 2018, replaces RN 0700 and RN 0710. |
| RN 17 FE | Basis ACEA C5, like RN 17 + fuel saving. |
| VW 500 00 | Multigrade oil with viscosity classes SAE 5W-X/10W-X, replaced by VW 501 01 |
| VW 501 01 | Multigrade oil with viscosity classes SAE 5W-X/10W-X, replaced by VW 502 00 |
| VW 502 00 | Multigrade oil for higher requirements |
| VW 503 00 | Longlife specification for gasoline engines, basis ACEA A1, viscosity classes 0W-30/5W-30 |
| VW 503 01 | Longlife specification for supercharged gasoline engines, viscosity class 5W-30 |
| VW 505 00 | Multigrade oil for naturally aspirated and turbocharged diesel engines |
| VW 505 01 | Multigrade oil for pump-nozzle motors, basis ACEA B4, viscosity class 5W-40 |
| VW 506 00 | Longlife specification for turbocharged diesel engines, viscosity class 0W-30 |
| VW 506 01 | Longlife specification for pump nozzle motors |
| INFO: All VW releases from 500,000 to 506 01 will be replaced by VW 504 00 and VW 507 00 (except R5 and V10 TDI engines before 06/2006) | |
| VW 504 00 | Longlife III – Specification for gasoline engines with and without longlife service |
| VW 507 00 | Longlife III – Specification for diesel engines with and without longlife service |
| VW 508 00 | Longlife IV – Specification for gasoline engines with and without longlife service, not backwards compatible, viscosity class SAE 0W-20 |
| VW 509 00 | Longlife IV – Specification for diesel engines with and without longlife service, not backwards compatible, viscosity class 0W-20 |
| VW 511 00 | Specification for high-performance gasoline engines with particulate filter, only for selected engines |
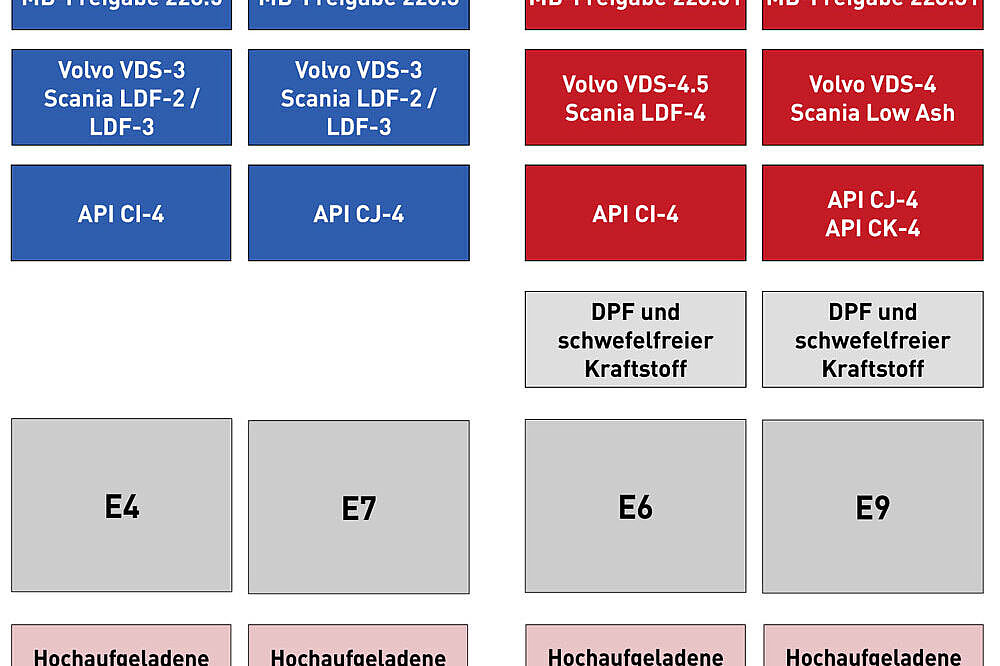
Commercial vehicle manufacturer specifications
European vehicle manufacturers base their prescribed manufacturer specifications on the ACEA or API engine tests. In order to achieve a manufacturer approval for a certain oil, in addition to the respective ACEA/API test procedure, further motor tests and requirements must be fulfilled.
Basic classification of commercial vehicle manufacturer specifications
| 18-1804 FE | Basis ACEA E4/E5 with TBN content >14 |
| 18-1804 TLS E6 | Basis ACEA E6 with TBN content >13 |
| 18-1804 T2 E7 | Basis ACEA E7 with TBN content >14 |
| 18-1804 TLS E9 | Basis ACEA E9 or API CJ-4 |
| 18-1804 TFE | Basis ACEA E4/E7 with TBN content >16 |
| 18-1804 TLV LS | Special development for IVECO Stralis Euro 6 engines equipped with fuel saving package FEP1, viscosity class 0W-20 |
| 18-1809 NG2 | Basis ACEA E6 with TBN content >12 viscosity class 5W-30 and 10W-40 for CNG engines |
| 18-1811 SC1 | Basis ACEA C2, with TBN >7, viscosity class 5W-30, for vans from MY 2009 |
| 18-1811 SC1 LV | Basis ACEA C2, with TBN >7, viscosity class 0W-30, for vans model year 2014–2021 |
| Volvo VDS | Basic API CD/CE, maintenance intervals up to 50,000 km possible |
| Volvo VDS-2 | Basis ACEA E7, maintenance intervals up to 60,000 km possible |
| Volvo VDS-3 | Basis ACEA E5, maintenance intervals up to 100,000 km possible |
| Volvo VDS-4 | Basis API CJ-4, short-distance, low-ash |
| Volvo VDS-4.5 | Basis API CK-4, long-distance, backwards compatible |
| Volvo VDS-5 | Basis API FA-4, lowered HTHS viscosity, not backwards compatible, for selected engines only |
| Scania LDF | Basis ACEA E5 |
| Scania LDF-2 | Basis ACEA E7 can be used from Euro 4 |
| Scania LDF-3 | Basis ACEA E7 can be used from Euro 5, extended change interval |
| Scania LDF-4 | Basis ACEA E6 usable from Euro 6, extended change interval, fuel saving, only for selected engines |
| Scania Low Ash | Basis ACEA E6/E9 (low-ash) |
| M3275 | SHPD engine oil, change interval up to 60,000 km possible |
| M3277 | UHPD engine oil, change interval up to 80,000 km possible |
| M3377 | Higher cleanliness/deposits requirements for M3277, change interval as per display |
| M3477 | Same as M3277 but low-ash for Euro 5 engines with DPF |
| M3677 | Euro 6 engines with DPF, change intervals up to 120,000 km possible |
| M3977 | For Euro 6 New Generation engines with fuel savings, viscosity class 5W-20, not backwards-compatible |
INFO: The separation of Daimler Truck AG (DTAG) and Mercedes-Benz Group AG (MBAG) has forced DTAG to change its fluid specifications. DTAG is therefore introducing the DTFR (Daimler Truck Fluid Release) specifications.
In future, engine oil specifications can be identified by the number 15, e.g. DTFR15C110 for sheet 228.51 or DTFR15B110 for sheet 228.3.
| MB approval 228.1 | Basis ACEA E2 + further engine tests |
| MB approval 228.3 | Basis ACEA E7 + further engine tests |
| MB approval 228.5 | Basis ACEA E4 + further engine tests, extended change interval |
| MB approval 228.31 | Basis ACEA E9 + further engine tests, DPF suitable |
| MB approval 228.51 | Basis ACEA E6 + further engine tests, DPF suitable, extended change interval |
| MB approval 228.61 | Basis API FA-4 + further engine tests |
INFO: 2 digits after the point = ash-reduced for exhaust gas treatment system
| RD(RD-2 | Basis ACEA E3 + Volvo VDS-2 |
| RLD/RLD-2 | Basis ACEA E9 + Volvo VDS-3 |
| RLD-3 | Basis ACEA E9 + Volvo VDS-4 |
| RLD-5 | Basic API FA-4 + Volvo VDS-5 for Euro 6d engines, not backwards compatible |
| RXD | Basis ACEA E7 + Volvo VDS-3 |
| RGD (Gas) | Basis ACEA E6 + Volvo VDS-3 + TBN > 8 |
Motorcycle manufacturer specifications
Motorcycle manufacturers largely dispense with their own oil specifications. They rely on the engine tests defined by API or JASO to determine the oil quality. In addition to determining the oil quality, for motorbikes that are equipped with clutches running in oil baths (wet clutch), higher requirements of shear stability, burning behavior and friction behavior have to be fulfilled.
Whether an oil fulfills these properties can be found out via the JASO specification (see JASO engine oil classification), which has to be listed under the approvals.
There is a European ISO standard for 2-stroke engine oils, which is comparable to the JASO 2-stroke classification.
| ISO-L-EGB | as JASO FB |
| ISO-L-EGC | as JASO FC |
| ISO-L-EGD | as JASO FD |



